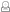multiple Gradient Buttons with CSS3
What Is So Cool About These Buttons?
- Pure CSS: no image or Javascript is used.
- The gradient is cross-browser supported (IE, Firefox 3.6, Chrome, and Safari).
- Flexible and scalable: button size and rounded corners can be adjusted by changing the font size and padding values.
- It has three button states: normal, hover, and active.
- It can be applied to any HTML element: a, input, button, span, div, p, h3, etc.
- Fallback: if CSS3 is not supported, it will display a regular button (no gradient and shadow).
Preview
The image below shows how the button will display in different browsers.
Button States
- normal state = gradient with border and shadow styles.
- hover = darker gradient
-
active = gradient is reversed, 1px down, and darker font color as well.

General Styles For The Button
The following code is the general styles for the .button class. I use em value in the padding and border-radius property to make it scalable base on the font-size. To adjust the rounded corners and button size, simply change the border-radius, font-size and padding values. For example: I can make a smaller button by decreasing the font-size and padding values.
.button {
display: inline-block;
outline: none;
cursor: pointer;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
font: 14px/100% Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
padding: .5em 2em .55em;
text-shadow: 0 1px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.3);
-webkit-border-radius: .5em;
-moz-border-radius: .5em;
border-radius: .5em;
-webkit-box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2);
-moz-box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2);
box-shadow: 0 1px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2);
}
.button:hover {
text-decoration: none;
}
.button:active {
position: relative;
top: 1px;
}

Color Gradient Styles
The code below is the CSS styling for the orange button. The first background line is a fallback for the non-CSS3 browsers, the second line is for Webkit browsers, the third line is for Firefox, and the last line is a gradient filter that is only read by Internet Explorer.
.orange {
color: #fef4e9;
border: solid 1px #da7c0c;
background: #f78d1d;
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, from(#faa51a), to(#f47a20));
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #faa51a, #f47a20);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#faa51a', endColorstr='#f47a20');
}
.orange:hover {
background: #f47c20;
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, from(#f88e11), to(#f06015));
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #f88e11, #f06015);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#f88e11', endColorstr='#f06015');
}
.orange:active {
color: #fcd3a5;
background: -webkit-gradient(linear, left top, left bottom, from(#f47a20), to(#faa51a));
background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #f47a20, #faa51a);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient(startColorstr='#f47a20', endColorstr='#faa51a');
}

How To Use My Buttons?
Lets say you like the blue button and want to use it on your page:
- First, copy the .button and .blue CSS
-
Then, add class="button blue" to the HTML element where you want the button to be (eg.
<a href="#" class="button blue">Button</a>). The CSS classes can be applied to any element such as link, p, span, div, input, button, etc.
The article source:http://webdesignerwall.com/tutorials/css3-gradient-buttons
You might also like
Tags
accordion accordion menu animation navigation animation navigation menu carousel checkbox inputs css3 css3 menu css3 navigation date picker dialog drag drop drop down menu drop down navigation menu elastic navigation form form validation gallery glide navigation horizontal navigation menu hover effect image gallery image hover image lightbox image scroller image slideshow multi-level navigation menus rating select dependent select list slide image slider menu stylish form table tabs text effect text scroller tooltips tree menu vertical navigation menu

 Subscribe
Subscribe Follow Us
Follow Us 13 years ago
13 years ago 17057
17057 4940
4940